

Steel making operation in the basic oxygen furnace (BOF) is also sometimes called basic oxygen steel making (BOS). Which is the best furnace for steel making? A large range of variation in the proportions of hot metal and scrap are possible in electric arc furnace steelmaking.
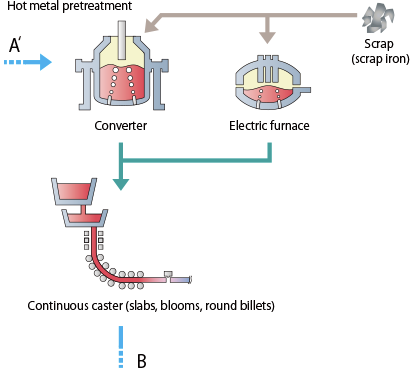
The LD converter process is characterized by the fact that it functions with 80 % to 90 % liquid hot metal and 10 % to 20 % cooling scrap as its metallic charge. How is an LD converter different from an arc furnace? How does a basic oxygen furnace make steel?īasic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) steel making or Basic Oxygen Furnace Steelmaking (BOS) or Linz-Donawitz-Verfahren steelmaking or the oxygen converter process is a method in which both molten pig iron and steel scrap are converted into steel with the oxidizing action of oxygen blown into the melt under a basic slag.

The quality of the iron ore is mainly determined by its composition a high iron content and low sulphur and phosphorus contents are favorable. Iron ore is a mineral aggregate that can be converted economically into iron. Steel is produced from iron ore or scrap. The raw materials for steelmaking are mined and then transformed into steel using two different processes: the blast furnace/basic oxygen furnace route, and the electric arc furnace route. Steel is made from iron ore, a compound of iron, oxygen and other minerals that occurs in nature. Both are accomplished by melting the iron ore at a very high temperature (1,700 degrees Celsius or over 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit) in the presence of oxygen (from the air) and a type of coal called coke. To make steel, the iron needs to be separated from the oxygen and a tiny amount of carbon needs to be added. Since there was no cooling effect from inert nitrogen gas present in air, any heat not lost to the off-gas… How is iron turned into steel? Use in steel production The Linz-Donawitz (LD) process, developed in Austria in 1949, blew oxygen through a lance into the top of a pear-shaped vessel similar to a Bessemer converter. Use in steel production As the ultimate development of the Bessemer/Thomas process,… The Linz-Donawitz (LD) process, developed in Austria in 1949, blew oxygen through a lance into the top of a pear-shaped vessel similar to a Bessemer converter. The blast furnace is the first step in producing steel from iron oxides. Steel is primarily produced using one of two methods: Blast Furnace or Electric Arc Furnace. Composition wise it is similar to blast furnace gas but with lesser percentage of nitrogen in it. It is a byproduct gas produced during the production of liquid steel in a basic oxygen furnace (converter), where impurities of hot metal are oxidized with oxygen gas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
